Featured publications
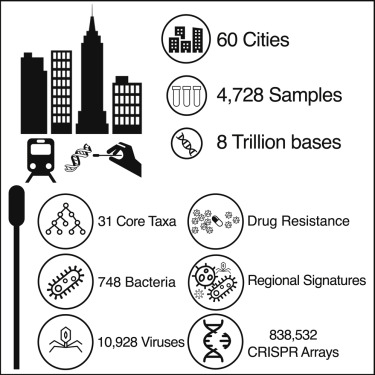
A global metagenomic map of urban microbiomes and antimicrobial resistance
David Danko, Daniela Bezdan, Evan E Afshin, Sofia Ahsanuddin, Chandrima Bhattacharya, Daniel J Butler, Kern Rei Chng, Daisy Donnellan, Jochen Hecht, Katelyn Jackson, Katerina Kuchin, ..., Alina Frolova, ..., Christopher E Mason, International MetaSUB Consortium
We present a global atlas of 4,728 metagenomic samples from mass-transit systems in 60 cities over 3 years, representing the first systematic, worldwide catalog of the urban microbial ecosystem. This atlas provides an annotated, geospatial profile of microbial strains, functional characteristics, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) markers, and genetic elements, including 10,928 viruses, 1,302 bacteria, 2 archaea, and 838,532 CRISPR arrays not found in reference databases.
Cell, 2021, 184(13), 3376-3393.e17.
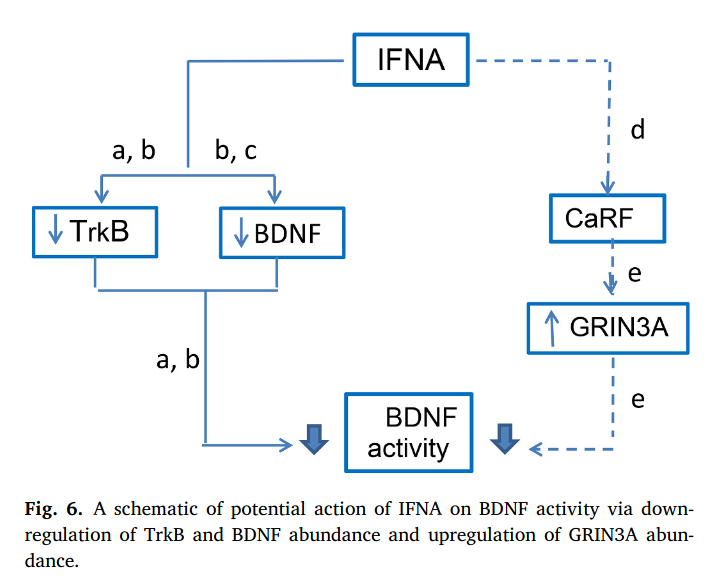
A new insight into mechanisms of interferon alpha neurotoxicity: Expression of GRIN3A subunit of NMDA receptors and NMDA-evoked exocytosis
M. Obolenskaya, V. Dotsenko, O. Martsenyuk, S. Ralchenko, O. Krupko, A. Pastukhov, N. Filimonova, D.Starosila, S. Chernykh, T. Borisova
The molecular mechanisms of interferon α neurotoxicity during the high-dose therapy are unknown. By bioinformatics approach, we predicted the gene Grin3α as a new potential target gene of IFNA. IFNA intracranial administration increased Grin3a expression and classical IFNA-target genes in the mouse brain. IFNA induces increased NMDA-evoked neurotransmitters release and does not affect neurotransmitters accumulation.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021;110:110317.
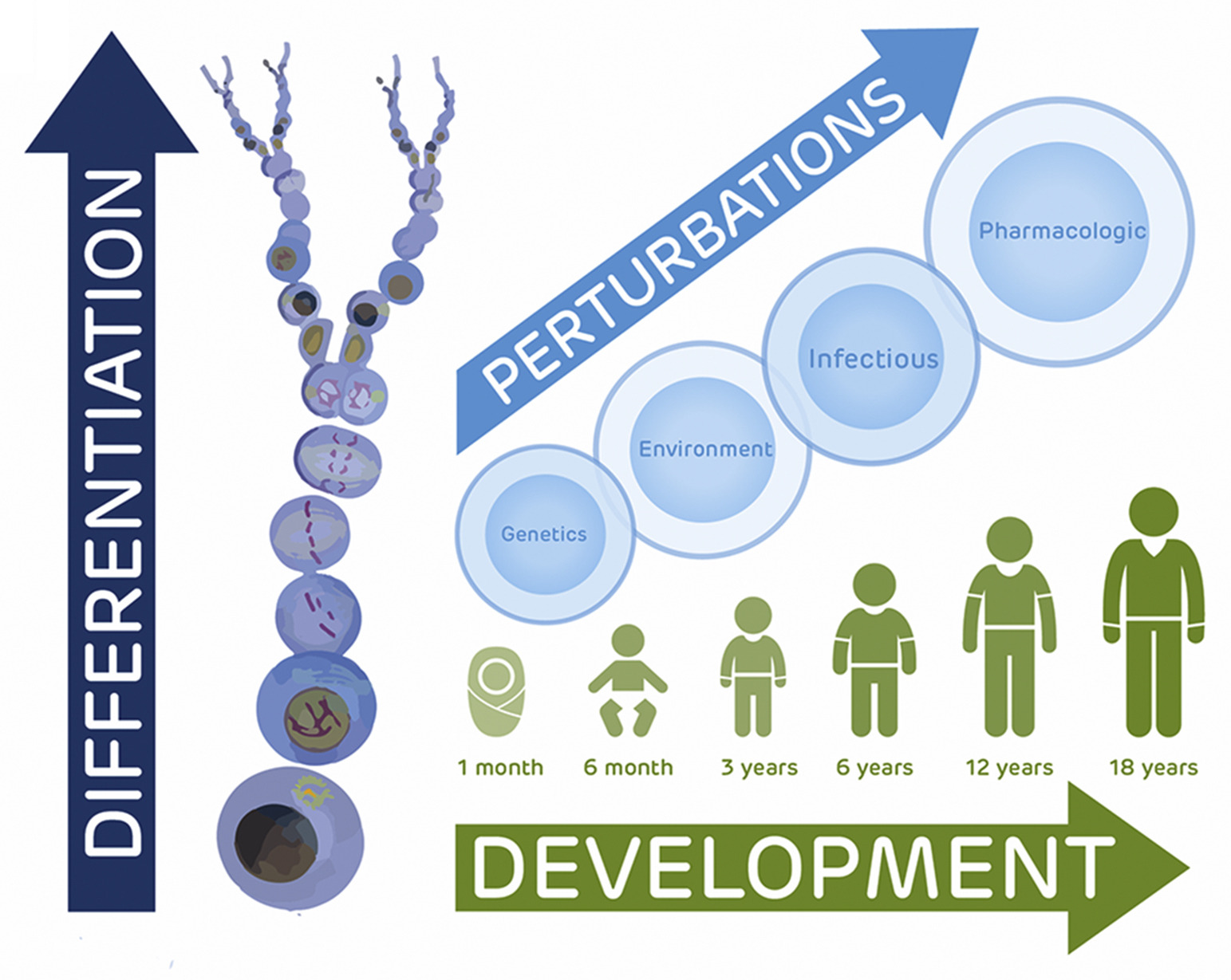
The Pediatric Cell Atlas: Defining the Growth Phase of Human Development at Single-Cell Resolution
Deanne M.Taylor, Bruce J.Aronow, Kai Tan, Kathrin Bernt, Nathan Salomonis, Casey S Greene, Alina Frolova, ..., Peter S White
We discuss here the case for a Pediatric Cell Atlas as part of the Human Cell Atlas consortium to provide single-cell profiles and spatial characterization of gene expression across human tissues and organs. Such data will complement adult and developmentally focused HCA projects to provide a rich cytogenomic framework for understanding not only pediatric health and disease but also environmental and genetic impacts across the human lifespan.
Cell, 2021, 184(13), 3376-3393.e17.
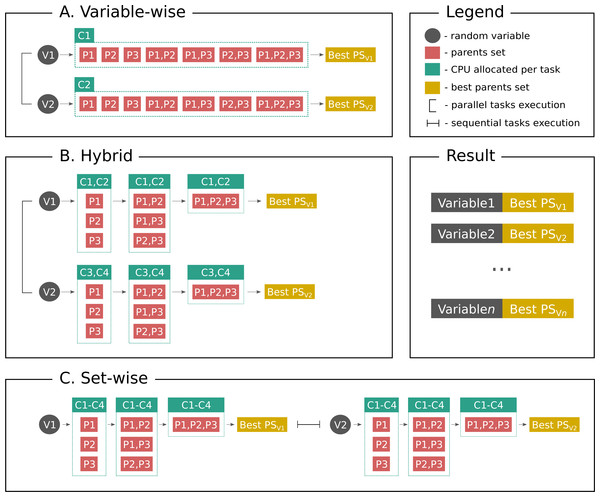
Distributed Bayesian networks reconstruction on the whole genome scale
Alina Frolova, Bartek Wilczyński
In the present paper we propose parallelized algorithm designed for multi-core and distributed systems and its implementation in the improved version of BNFinder—tool for learning optimal Bayesian networks. Our benchmarking results on realistic datasets indicate that the tool should be useful to a wide audience of researchers interested in discovering dependencies in their large-scale transcriptomic datasets.
PeerJ, 2017, 6:e5692.
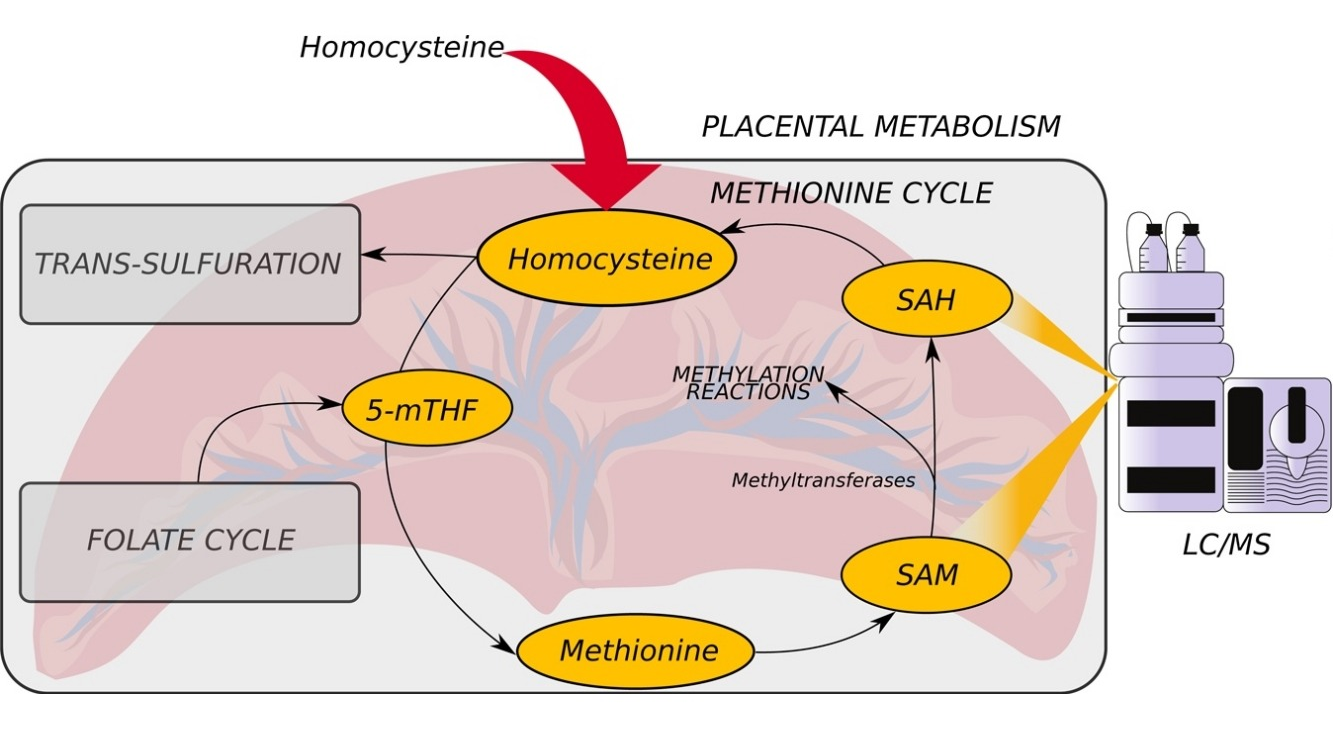
Quantification of S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in human placenta and placental explants under homocysteine treatment
R. Rodriguez, O. Vakulenko, S. Ralchenko, A. Kostiuk, L. Porublyova, I. Konovets, I. Voronina, M. Obolenskaya
Cost- and time-effective HPLC/MS method was developed for analysis of SAM and SAH concentration in human placenta. The concentration of SAM and SAH depends on the concentration of homocysteine and amino acids cirtical for one carbon metabolism. The fraction of each methyltransferase maximal velocity depends on its MIchaelis constant and SAM and SAH concentration.
International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2017, 421, pp.279-284.
The start of systems biology in Ukraine
Obolenskaya M. Yu., Tokovenko B. T., Kuklin A. V., Frolova A. O., Rodriguez R. R., Dotsenko V. A., Dragushchenko O. O.
The first laboratory of Systems Biology in Ukraine (IMBIG NASU) represents a track record of its scientific results. They include the pioneered development of a web-based tool for genome-wide surveys of eukaryotic promoters for the presence of transcription factors binding sites (COTRASIF); the deciphered mechanisms of the fine-tuned and balanced response of primary hepatocytes to interferon alpha levels recorded after partial hepatectomy; the elaboration of a novel method of gene regulatory network inference compatible with GRID environment and the development of a stoichiometric model of folate-related one carbon unit metabolism in human placenta and its application for the characteristics of the system’s behavior as a whole at different human pathologies.
Biopolym. Cell. 2014; 30(1):16-24.
Publications by year
- Wu, Jun, et al. “Annotating Unknown Species of Urban Microorganisms on a Global Scale Unveils Novel Functional Diversity and Local Environment Association.” Environmental Research, vol. 207, 2022, p. 112183.
- Danko, David, et al. “A Global Metagenomic Map of Urban Microbiomes and Antimicrobial Resistance.” Cell, vol. 184, no. 13, 2021, pp. 3376–93.
- Lykhenko, O. K., et al. “Changes in the Human Placental Transcriptome during the Physiological Course of Pregnancy.” Biopolymers & Cell, vol. 37, no. 1, 2021.
- Birukov, Anna, et al. “Myocardial Evaluation of Post-Preeclamptic Women by CMR: Is Early Risk Stratification Possible?” Cardiovascular Imaging, vol. 13, no. 5, 2020, pp. 1291–93.
- Taylor, Deanne M., et al. “The Pediatric Cell Atlas: Defining the Growth Phase of Human Development at Single-Cell Resolution.” Developmental Cell, vol. 49, no. 1, 2019, pp. 10–29.
- Nonn, Olivia, et al. “Placental CX3CL1 Is Deregulated by Angiotensin II and Contributes to a pro-Inflammatory Trophoblast-Monocyte Interaction.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 20, no. 3, 2019, p. 641.
- Birukov, Anna, et al. “Regulatory Antibodies against GPCR in Women Ten Years after Early-Onset Preeclampsia.” Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed), vol. 24, no. 8, 2019, pp. 1462–77.
- Frolova, Alina, and Bartek Wilczyński. “Distributed Bayesian Networks Reconstruction on the Whole Genome Scale.” PeerJ, vol. 6, 2018, p. e5692.
- Frolova, Alina, and Maria Obolenska. “Integrative Approaches for Data Analysis in Systems Biology: Current Advances.” 2016 II International Young Scientists Forum on Applied Physics and Engineering (YSF), IEEE, 2016, pp. 194–98.
